Understanding muscle contractions are important if you are on a fitness journey that includes muscle growth, strength, fat loss, mobility and sports specific training. Once you understand the basics of muscle contraction I am convinced that you will speed up your ability to meet your goals. And I say basics because you don’t need to be a fit pro, a scientist or professional athlete to know your own body. Hopefully a little bit of reading of articles that leave out the jargon can help you to understand. So let’s jump straight in!
Your muscles perform three types of contractions when you exercise.
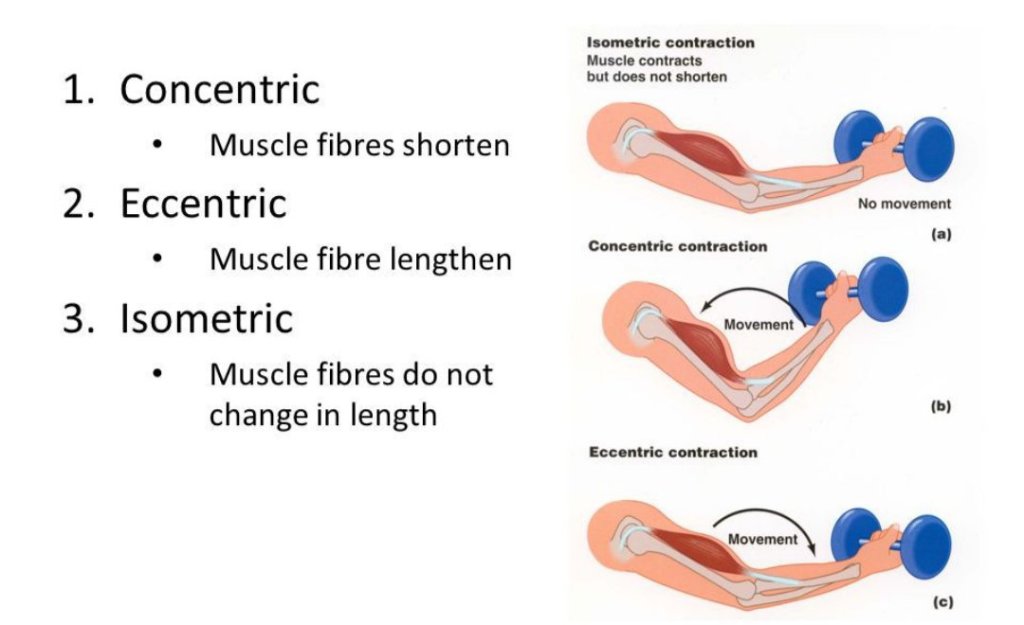
* Concentric
* Eccentric
* Isometric
A concentric movement shortens the muscle to force an object to move. Think of the bicep curl. As you force the weight towards your shoulder your bicep shortens to create a squeeze.
An eccentric movement lengthens the muscle and stretches the muscle fibres. Imagine the lowering of the weight during a bicep curl or the squatting part of a squat or leg press. This phase of the rep is regarded as the part that induces the most muscle growth as the muscle fibres are fully activated in lowering a weight under control. This is where delayed onset of muscle soreness (DOMS) are most like to occure and specific eccentric training is a popular training phase for many athletes.
An isometric movement is a contraction that does not require muscle to lengthen or shorten. Think of a plank or wall sit. There are no reps that use concentric or eccentric movement. These are particularly useful when sparing the joints from discomfort or injury but still strengthening the muscle.
Developing an understanding of these muscle contractions will give you a greater appreciation of time under tension (TUT). Powering through 12 reps in 15 seconds is fairly straightforward. However, this is not the best way to train. Once you imagine the muscle lengthening and shortening through repeated exposure to the load of the weight then you can create a clear ‘mind to muscle’ pathway. You begin to think about each rep rather than just move a weight from A to B and it might need you to cut out the ego lift and go lighter. Just because you’re benching 100k doesn’t mean your muscle has gotten much out of the process. If you aren’t in control of your muscle contractions then your target muscle is unlikely to feel the need to change.
I ask my online trainees what their rate of perceived exertion (RPE) is after each exercise. As I’m not physically stood next to these clients I cannot see how easy or difficult they found the activity. If they are rating their workout at around 5/10 I would ask them to slow the tempo of each rep before adding more load in an attempt to challenge them to a high exertion level.
TUT and muscle hypertrophy

Earlier I mentioned time under tension as a significant factor in muscle development. Longer TUT will create a more challenging experience and much more rewarding for muscle hypertrophy. If I were to learn French for ten minutes a day I would get much less knowledge of the language than if I were to learn French for 30 minutes.
So, if I were to complete a set in ten seconds I would get much less chance to elicit muscle growth than if I were to complete a set in 30 seconds. Every rep and set is an opportunity for muscle growth. Moving a heavy object is easy. Thinking about it requires muscle engagement.
I hope that this article helps. I have tried to remove unnecessary jargon as I believe that resistance training should be enjoyed by everyone and we shouldn’t need a physiology degree to do it. And not just do it, but do it to ensure you get the benefits from it!
















